When you have celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder where the body attacks the small intestine in response to gluten. Also known as gluten-sensitive enteropathy, it’s not a food allergy or a choice—you can’t just "try harder" to eat gluten. Your immune system sees gluten as an invader, and over time, it flattens the tiny finger-like villi in your gut that absorb nutrients. That’s why people with celiac disease often feel tired, bloated, or even lose weight despite eating normally.
Many people mistake celiac disease for gluten intolerance, a non-autoimmune reaction to gluten that causes discomfort but doesn’t damage the intestine. But celiac is different. It shows up in blood tests, can be confirmed with a biopsy, and if left untreated, raises your risk for osteoporosis, anemia, and even certain cancers. It’s not something you grow out of. Once diagnosed, the only treatment is a strict, lifelong gluten-free diet, avoiding wheat, barley, rye, and hidden sources like sauces, medications, and even some cosmetics. And no, "gluten-free" labeled snacks don’t make it easy—cross-contamination in kitchens or restaurants can still trigger symptoms.
What’s surprising is how many people live with undiagnosed celiac disease. Symptoms vary wildly: some get diarrhea and stomach pain, others have joint aches, skin rashes, or just chronic fatigue. Kids might fail to grow properly. Women may struggle with infertility. That’s why doctors now test for it more often, especially if you have a family history or another autoimmune condition like thyroid disease or type 1 diabetes. It’s not just about what you eat—it’s about how your body reacts at a cellular level.
Below, you’ll find real, practical guides on managing celiac disease—not just diet tips, but how it connects to other health issues like bone loss, medication safety, and digestive complications. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or helping someone who is, these posts cut through the noise and give you what actually works.
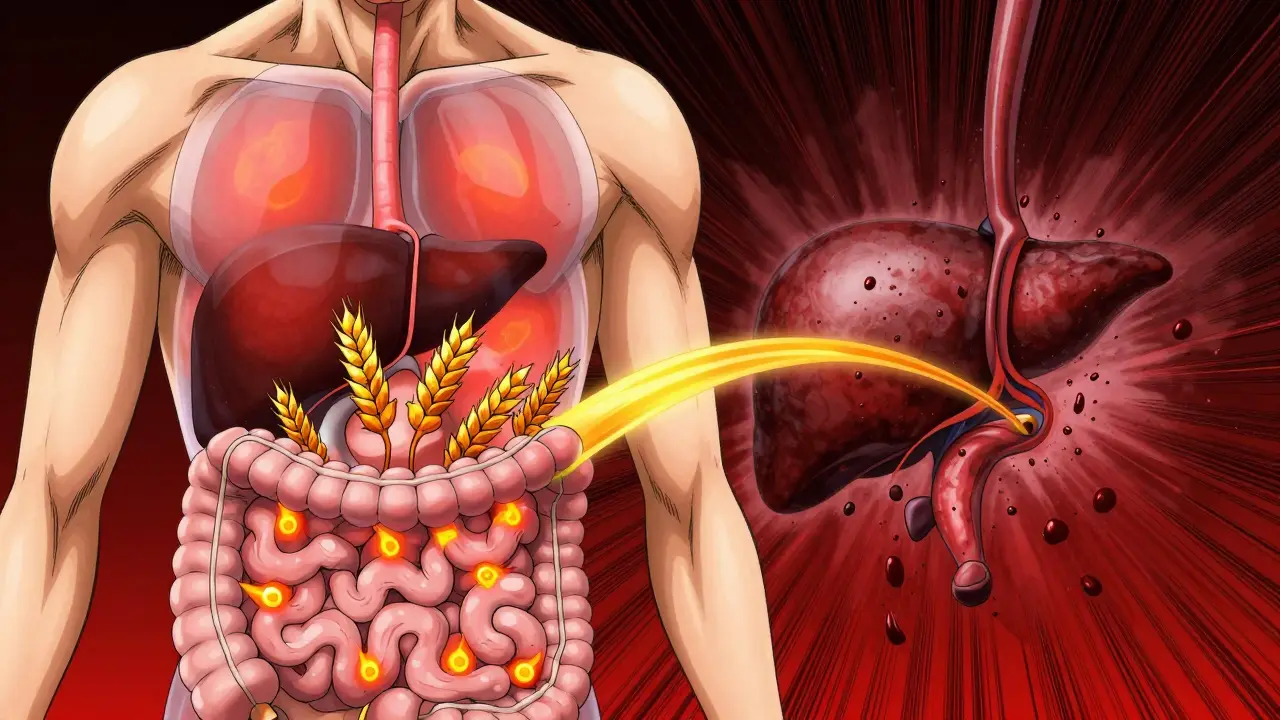
Celiac disease can cause elevated liver enzymes and fatty liver even without digestive symptoms. A strict gluten-free diet often reverses liver damage-but processed gluten-free foods can make it worse. Learn how the two are linked and what to do next.
View more
Rifaximin helps celiac patients with ongoing symptoms like bloating and diarrhea by targeting bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine-without disrupting the rest of the body. It's not a cure, but a targeted tool for healing.
View more