Memantine is a prescription medicine most often used for moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease. It won’t cure dementia, but it can help with memory, thinking, and daily function for some people. If you or a loved one are starting memantine, it helps to know what to expect and how to use it safely.
Memantine blocks overactive signals in the brain tied to a chemical called glutamate. Too much glutamate can harm brain cells, so memantine calms that activity. That action can reduce symptoms like confusion or trouble with daily tasks in some patients.
Common side effects include dizziness, headache, constipation, and tiredness. A smaller number of people experience increased confusion, hallucinations, or mood changes. Most side effects are mild and show up during dose changes. If serious side effects appear, contact the prescriber right away.
Doctors usually start memantine at a low dose and raise it slowly. A typical plan begins at 5 mg once daily and works up to 20 mg per day split into two doses. Kidney function matters: people with reduced kidney function often need a lower dose. Don’t change dose or stop the drug without checking with the prescriber.
Take memantine exactly as written. You can take it with or without food. If you miss one dose, take it when you remember unless it’s close to the next dose—then skip the missed dose. Keep a pill box or set a phone reminder to avoid missed doses.
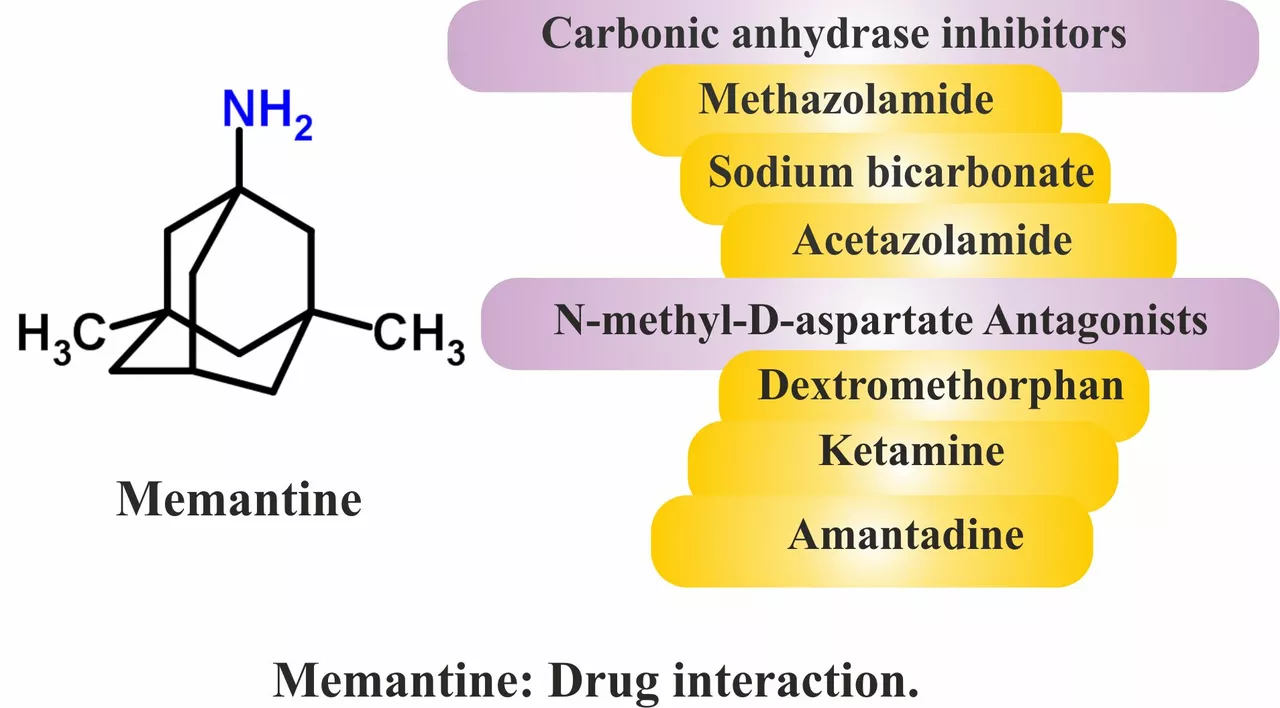
Watch for interactions. Memantine can interact with other drugs that affect brain signaling (for example, certain NMDA antagonists) and with medications that change urine pH, since kidney clearance affects memantine levels. Tell your prescriber about all meds, supplements, and over-the-counter drugs you use—especially strong antacids, dextromethorphan, or drugs that change kidney function.
Practical caregiving tips: track mood, sleep, appetite, and daily skills on a short checklist so you notice changes fast. Bring that checklist to follow-up visits. Keep med bottles in their original packaging and store them away from heat and moisture. If the person with dementia wanders or forgets doses, set up supervised dosing.
When buying online, only use licensed pharmacies and check for a real phone number and pharmacist access. Never buy meds from a site that skips prescriptions. If cost is an issue, ask the prescriber about patient assistance programs or local pharmacy discount cards.
If you have questions about memantine’s role in care, ask the prescriber for specific goals to watch for in 3 months—improved daily routines, less confusion at key times, or reduced agitation are reasonable targets. That makes it easier to judge whether the medicine is helping and worth continuing.
As a blogger, I recently researched Memantine dosage and administration guidelines. From what I gathered, Memantine is typically prescribed for patients suffering from moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. The recommended starting dose is usually 5 mg once daily, gradually increasing to a maximum of 20 mg per day. It's important to note that doctors may adjust the dosage based on individual patient needs and tolerability. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your medication regimen.
View more