Understanding Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
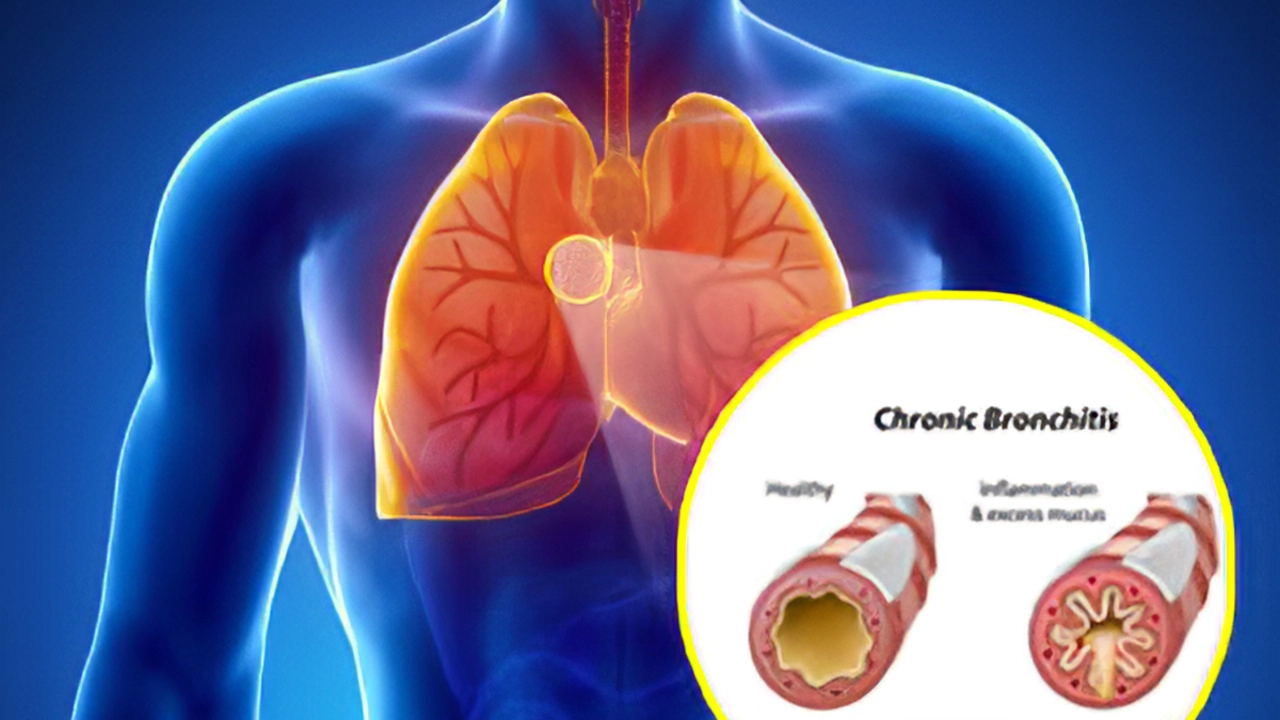
Before diving into the relationship between climate change and obstructive pulmonary disease, it's crucial to first have a basic understanding of what obstructive pulmonary disease is. Obstructive pulmonary disease is a term used to describe chronic lung diseases that make it difficult to breathe, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and bronchiectasis. These conditions are characterized by an obstruction in the airflow, which leads to shortness of breath, coughing, and other respiratory symptoms.
Obstructive pulmonary diseases can have a significant impact on the quality of life for those affected. These conditions often require ongoing medical treatment and management, and in some cases, they can even be life-threatening. With that in mind, it's crucial to explore the potential impact of climate change on these diseases and what it may mean for the millions of people living with them worldwide.
The Connection between Climate Change and Air Pollution
One of the primary ways in which climate change affects obstructive pulmonary disease is through its impact on air pollution. As temperatures rise due to climate change, there is an increase in the production of ground-level ozone, a harmful air pollutant that can exacerbate existing respiratory conditions. Ozone is formed when pollutants from vehicle exhaust, power plants, and other sources react with sunlight, and higher temperatures can speed up this process.
Additionally, climate change can contribute to more frequent and severe wildfires, which release large amounts of particulate matter and other pollutants into the air. This can further worsen air quality and have detrimental effects on individuals with obstructive pulmonary diseases.
Extreme Weather Events and Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Climate change is also associated with an increase in the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, storms, and floods. These events can have a variety of negative impacts on those with obstructive pulmonary disease. For example, extreme heat can exacerbate respiratory symptoms in individuals with COPD or asthma by increasing airway inflammation and reducing lung function.
Moreover, extreme weather events can disrupt access to healthcare services, making it challenging for individuals with obstructive pulmonary disease to receive the necessary medical care and support. This can result in a worsening of their condition and an increased risk of complications.
Climate Change and Increased Allergens
Another way in which climate change can affect obstructive pulmonary disease is by increasing the levels of allergens in the environment. Warmer temperatures and higher levels of carbon dioxide can cause plants to produce more pollen, a common allergen that can trigger asthma symptoms in sensitive individuals. This increase in pollen can lead to a higher prevalence of allergic asthma and exacerbate existing cases.
Furthermore, climate change can also lead to longer and more intense allergy seasons, resulting in prolonged exposure to allergens and a greater likelihood of experiencing respiratory symptoms for those with allergic asthma.
Climate Change and Respiratory Infections
Climate change can also have an impact on the spread of respiratory infections, which can be particularly problematic for individuals with obstructive pulmonary disease. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect the transmission of viruses and bacteria that cause respiratory infections, such as the flu and pneumonia. These infections can be severe in those with pre-existing respiratory conditions, as they can further impair lung function and increase the risk of complications.
Moreover, warmer temperatures can also lead to an increase in the prevalence of mold and fungi, which can cause respiratory infections in susceptible individuals. These infections can be especially dangerous for those with obstructive pulmonary disease, as they can exacerbate existing symptoms and further damage the lungs.
Adapting to Climate Change to Protect Lung Health
Given the numerous ways in which climate change can impact obstructive pulmonary disease, it's essential to take steps to adapt and protect the health of those affected. This can include implementing strategies to reduce air pollution, such as transitioning to cleaner sources of energy and promoting sustainable transportation options.
Additionally, healthcare providers can work to improve the resilience of their services in the face of extreme weather events, ensuring that individuals with obstructive pulmonary disease have access to the care they need. This might involve developing emergency preparedness plans and investing in infrastructure to withstand the impacts of climate change.
Preventing and Managing Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in a Changing Climate
While adapting to climate change is important, it's also crucial to focus on preventing and managing obstructive pulmonary disease in the context of a changing climate. This can include promoting public awareness about the link between climate change and respiratory health, as well as advocating for policies that address the root causes of climate change.
On an individual level, those with obstructive pulmonary disease can take steps to manage their condition and minimize the impact of climate change on their health. This might involve staying indoors on days with poor air quality, using air purifiers, and working closely with healthcare providers to ensure their treatment plan is up to date and effective.
Supporting Research and Innovation
Another crucial aspect of addressing the impact of climate change on obstructive pulmonary disease is supporting research and innovation in this field. This can involve investing in studies that explore the links between climate change and respiratory health, as well as the development of new treatments and interventions that can help those with obstructive pulmonary disease adapt to a changing climate.
By fostering a greater understanding of the relationship between climate change and obstructive pulmonary disease, we can work towards developing effective strategies to protect the health of those affected and ultimately create a more sustainable and healthy future for all.
Conclusion
In conclusion, climate change poses significant threats to those with obstructive pulmonary disease, from worsening air pollution and allergen levels to increasing the frequency and severity of extreme weather events. It's essential for individuals, healthcare providers, and policymakers to recognize these risks and work together to develop strategies to prevent, manage, and adapt to the impacts of climate change on respiratory health. By doing so, we can safeguard the well-being of millions of people living with obstructive pulmonary disease and create a healthier future for generations to come.

Subramaniam Sankaranarayanan
June 18, 2023 AT 14:32It is unsurprising that climate change exacerbates obstructive pulmonary disease, because the underlying physics are well‑established. Rising temperatures accelerate photochemical reactions, leading to higher ground‑level ozone, which directly irritates airway epithelium. Moreover, the increased frequency of wildfires injects fine particulate matter deep into the lungs, compromising mucociliary clearance. From an ethical standpoint, we must hold polluters accountable; the suffering of millions with COPD and asthma is a direct consequence of negligent emissions. The moral imperative is clear: societies that prioritize short‑term economic gain over public health are failing a basic duty to protect vulnerable citizens.
Kylie Holmes
June 26, 2023 AT 16:58Stay pumped, folks-every breath counts!
Jennifer Wees-Schkade
July 4, 2023 AT 19:25When considering mitigation strategies, it helps to look at the evidence from recent cohort studies. Patients with well‑controlled inhaler regimens still experience exacerbations on high‑ozone days, indicating that environmental control is as crucial as pharmacologic therapy. Public health officials should therefore prioritize real‑time air‑quality alerts for at‑risk populations. Additionally, community clinics can distribute portable air‑purifiers during wildfire seasons to reduce indoor pollutant load.
Fr. Chuck Bradley
July 12, 2023 AT 21:52Imagine a world where the sky itself betrays you, turning a simple walk outside into a perilous adventure. The drama of coughing fits amid a smog‑filled sunset is something no one signed up for, yet here we are, silently gasping for cleaner air.
Patrick Rauls
July 21, 2023 AT 00:18Yo, the link between climate shifts and lung health is real-no joke. Gotta keep an eye on those AQI numbers, especially when the heat waves roll in. If you’re feeling rough, a HEPA filter can make a big diff. Stay safe out there! 🙂
Asia Lindsay
July 29, 2023 AT 02:45Great points above about air‑quality alerts. Building on that, many local health departments now offer free respirator fittings for seniors with COPD during wildfire events. Pairing those resources with tele‑medicine check‑ins can keep treatment plans on track when clinics are inaccessible. Keep pushing for community‑level support, and remember to celebrate small victories-like a day with clear skies!
Angela Marie Hessenius
August 6, 2023 AT 05:12One cannot overstate the intricate cascade of physiological disturbances that ensue when ambient air quality deteriorates under the pressure of a warming climate. The increase in tropospheric ozone, a by‑product of volatile organic compounds reacting under intensified solar radiation, initiates a chain reaction of oxidative stress within the bronchial epithelium. This oxidative burden not only precipitates acute inflammatory episodes but also accelerates the remodeling of airway structures, a hallmark of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease progression. Moreover, particulate matter-especially fine particles under 2.5 micrometers-possesses the insidious ability to penetrate deep into the alveolar sacs, where macrophage function is compromised, thereby fostering a microenvironment conducive to bacterial colonization and recurrent infections. Studies from the Global Burden of Disease project reveal a statistically significant correlation between rising average temperatures and heightened hospital admission rates for asthma exacerbations, a relationship that persists even after adjusting for socioeconomic variables. In addition to the direct physiological insult, climate‑driven alterations in pollen seasonality extend the temporal window of allergen exposure, further aggravating hyper‑responsive airways. The mounting evidence suggests that climate mitigation is not merely an environmental imperative but a public health necessity, particularly for populations already burdened by chronic respiratory ailments. Consequently, interdisciplinary collaboration between climatologists, pulmonologists, and policy makers becomes essential to devise adaptive strategies that safeguard lung health. These may include expanding green infrastructure to reduce urban heat islands, incentivizing the adoption of low‑emission transportation, and strengthening surveillance systems for air‑quality indices. The convergence of these efforts holds promise for attenuating the trajectory of disease burden, thereby improving quality of life for millions worldwide. In sum, the nexus between climate change and obstructive pulmonary disease is multifaceted, demanding a holistic, proactive response that transcends traditional medical interventions.
Julian Macintyre
August 14, 2023 AT 07:38While the preceding exposition admirably enumerates numerous pathophysiological mechanisms, it suffers from an excess of rhetorical flourish that detracts from analytical precision. A more disciplined approach would isolate the causative variables-namely ozone concentration, particulate matter PM2.5, and allergen load-and quantify their marginal effects using multivariate regression. Moreover, the assertion that “green infrastructure” will unequivocally mitigate exposure warrants empirical validation; retrospective cohort analyses have yielded mixed outcomes. Thus, the discourse would benefit from a tighter methodological framework, supported by robust statistical evidence rather than a cascade of qualitative assertions.
Patrick Hendrick
August 22, 2023 AT 10:05Keeping focus, folks, on actionable steps; use masks during spikes, check AQI apps, and stay hydrated!!!
abhishek agarwal
August 30, 2023 AT 12:32Exactly-those simple habits can make a massive difference, and there’s no excuse for ignoring them when the data are this clear.
Michael J Ryan
September 7, 2023 AT 14:58Hey all, just a quick reminder that many public libraries now host free workshops on using low‑cost air‑purifiers at home. These sessions are great for picking up practical tips without any jargon, and they’re perfect for folks who feel overwhelmed by the science.
Khalil BB
September 15, 2023 AT 17:25In a way, the air we breathe mirrors the choices we make-each breath a silent pact with the planet’s future.
Keri Shrable
September 23, 2023 AT 19:52Love the vibe here-let's keep the conversation bright and hopeful while we tackle the heavy stuff together
Destiny Hixon
October 1, 2023 AT 22:18Honestly, all this talk about “green solutions” is just a smokescreen while big polluters keep churning out carbon. We need real action now, not pretty slogans.
mike brown
October 10, 2023 AT 00:45Well, if we’re going to blame the climate for everything, maybe we should also blame it for the occasional traffic jam and the fact my coffee was too hot this morning. Just saying.
shawn micheal
October 18, 2023 AT 03:12Hey, I get the sarcasm, but let’s not dismiss the genuine health crises people are facing. A little empathy goes a long way, especially when the air gets nasty.
Stephen Jahl
October 26, 2023 AT 05:38The ontological interdependence of atmospheric thermodynamics and pulmonary pathophysiology mandates a rigorous interdisciplinary paradigm. Contemporary epidemiological models, predicated upon spatiotemporal variance in tropospheric aerosol optical depth, elucidate a statistically significant positive correlation (p < 0.01) with exacerbation frequency in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease cohorts. Moreover, the physicochemical transformation of volatile organic compounds under intensified solar insolation engenders secondary organic aerosols, which potentiate alveolar macrophage dysfunction via oxidative stress pathways, thereby degrading innate immunologic resilience. In light of these mechanistic insights, policy frameworks must transcend superficial emission caps, instituting quantifiable reductions in precursor gases such as NOₓ and SO₂, complemented by urban planning that attenuates heat island effects through albedo modification. Failure to operationalize such evidence‑based interventions will inexorably exacerbate morbidity and mortality indices, contravening both ethical imperatives and international health obligations.
gershwin mkhatshwa
November 3, 2023 AT 07:05Whoa, that was a heavy dose of jargon! Bottom line: cleaner air = healthier lungs, and we can actually make that happen if we push for smarter city designs and stricter emissions rules.
Louis Robert
November 11, 2023 AT 09:32Nice summary-keep it simple and actionable.
tim jeurissen
November 19, 2023 AT 11:58Just a quick note: in the earlier post, “obstructive pulmonary disease” should be capitalized as “Obstructive Pulmonary Disease” when used as a proper term; also, “air‑quality” is conventionally hyphenated.